Introduction
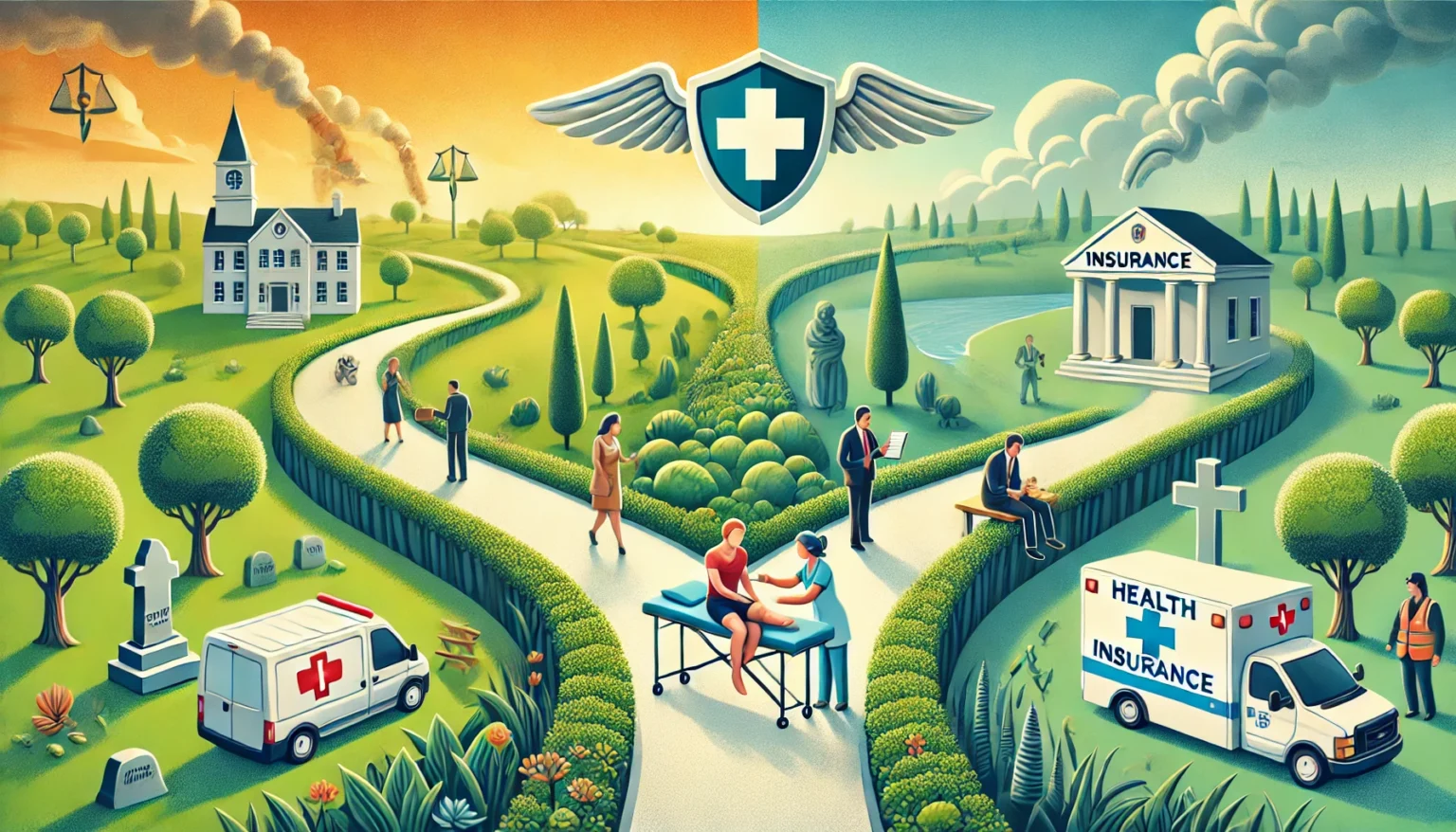
Subrogation is a term that might seem complex, but it plays a crucial role in the world of health insurance. When an insurance company pays for your medical expenses due to an injury or illness caused by another party, it often has the right to recover those costs from the responsible party. This process is known as subrogation.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about what is subrogation in health insurance, including how it works, its benefits, challenges, and how it impacts you as a policyholder.
Understanding Subrogation
Subrogation in health insurance is a legal concept where an insurance company steps into the shoes of the policyholder to seek reimbursement for medical expenses paid on their behalf. This right is established through the insurance policy agreement and is designed to prevent the insured from receiving a double recovery — being compensated twice for the same expenses.
Subrogation ensures that the party responsible for causing the injury or illness ultimately bears the financial burden, not the insurance company or the insured. It is a crucial process that helps insurance companies recover their losses and maintain lower premiums for policyholders.
Types of Subrogation
- Contractual Subrogation: This type is defined by the terms of the insurance policy, where the policyholder agrees that the insurer has the right to seek recovery from a third party.
- Equitable Subrogation: Rooted in fairness, this type allows the insurer to recover costs even without a specific agreement if it is just and reasonable.
- Statutory Subrogation: This type is established by law, where legal provisions grant the insurer the right to recover payments from third parties responsible for the injury.
How Subrogation Works in Health Insurance
The subrogation process begins when a health insurance company pays for medical expenses related to an injury or illness. If another party is found to be responsible for that injury — such as in a car accident or workplace incident — the insurance company can pursue reimbursement from the responsible party or their insurer.
Here’s a clear breakdown of the subrogation process:
- The insurance company pays the medical expenses for the insured.
- The insurer investigates the cause of the injury and identifies any responsible parties.
- If another party is found to be at fault, the insurer seeks reimbursement from that party’s insurance company.
- If the insured receives a settlement from the responsible party, the insurer may claim a portion of that settlement to cover their costs.
This process protects the insurer’s financial interests while ensuring that the person responsible for the injury is held accountable.
Real-Life Examples of Subrogation
Consider a scenario where you are injured in a car accident caused by another driver. Your health insurance pays for your medical treatment. Later, it is determined that the other driver was at fault. Your health insurance company can then pursue that driver’s auto insurance for reimbursement of the medical expenses it covered.
Another example is a workplace injury where an employee receives medical treatment covered by their health insurance. If the injury was caused by a third-party contractor’s negligence, the insurer may seek recovery from the contractor’s insurance.
Benefits of Subrogation
Subrogation offers several benefits to both insurers and policyholders:
- Cost Recovery: Insurance companies can recover their losses by holding the responsible party accountable.
- Lower Premiums: By recovering costs through subrogation, insurers can maintain more affordable premiums for their policyholders.
- Fairness: It ensures that the party responsible for causing the injury bears the financial burden.
Challenges and Considerations
While subrogation is beneficial, it is not without its challenges. Legal complexities can arise, especially when multiple parties are involved. Additionally, subrogation can delay settlement payments for the policyholder if the insurer asserts a subrogation claim against a settlement.
Waiver of Subrogation
A waiver of subrogation is a clause in an insurance policy where the insurer agrees not to seek reimbursement from a third party, even if that party is at fault. This is often used in situations where maintaining a business relationship is more important than pursuing recovery.
Conclusion
Understanding what is subrogation in health insurance is essential for every policyholder. It is a process that protects insurers’ financial interests, maintains lower premiums, and ensures fairness by holding the responsible parties accountable. Being aware of how subrogation works can help you navigate your health insurance policy more effectively and avoid unexpected financial obligations.
Other Articles
Phone Number Durostech: Company Overview and Contact Information
The Ultimate Guide to 1.5f8-p1uzt Texture: Features, Uses, Benefits, and Future
FA3020PF Westinghouse: Complete Guide to Features, Specs, Installation & Uses
Alyson Heather Belcourt Tattoo: The Soul of Artistic Expression in Ink