How Do Game Conservation Laws Affect Hunters?
Game conservation laws play a critical role in shaping how hunters interact with wildlife and the environment. These regulations are not only intended to preserve ecosystems but also to create a sustainable framework for hunting that benefits both nature and those who enjoy this traditional activity. This article explains in detail how game conservation laws affect hunters by regulating practices, ensuring safety, supporting wildlife management, and preserving opportunities for future generations.
I. Introduction to Game Conservation Laws
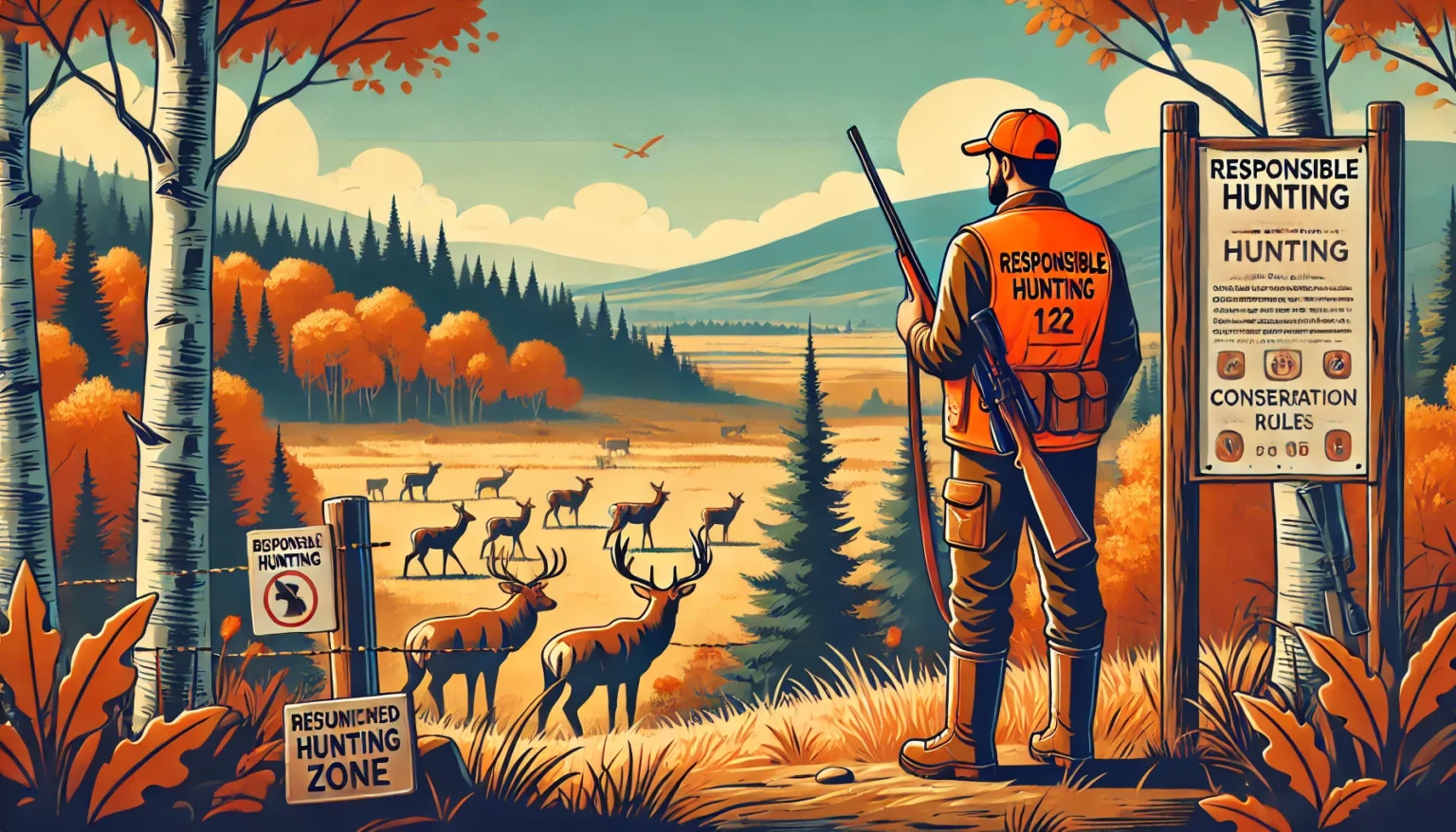
Game conservation laws are sets of rules established by governments or wildlife authorities to protect animal populations and their habitats. These laws manage hunting activities to ensure that wildlife is not overexploited. They also ensure ethical hunting practices and help maintain a balance in ecosystems. Understanding how game conservation laws affect hunters is crucial because it helps hunters comply with regulations, avoid penalties, and contribute positively to conservation efforts.
II. Key Components of Game Conservation Laws
Hunting Seasons:
One of the most essential elements of conservation laws is the regulation of hunting seasons. These seasons are carefully scheduled to avoid breeding or nesting times, allowing species to reproduce and maintain their populations. For example, deer hunting may be allowed in the fall when young deer are more independent, minimizing harm to reproduction cycles.
Bag Limits and Quotas:
Bag limits refer to the number of animals a hunter can legally harvest in a day or season. These are set based on scientific population data. For example:
| Species | Daily Limit | Seasonal Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Duck | 6 | 60 |
| White-tailed Deer | 1 | 5 |
| Turkey | 1 | 2 |
These quotas help prevent overhunting and allow wildlife populations to recover and thrive.
Licensing and Permits:
Hunters are typically required to purchase a license and sometimes additional permits for specific game. This system ensures that only trained and registered individuals engage in hunting, making enforcement easier. The fees from licenses often go directly toward conservation projects.
Approved Hunting Methods and Equipment:
Conservation laws dictate which hunting tools and techniques are permissible. For example, using silencers or hunting at night might be banned in certain areas to prevent unethical or dangerous behavior.
Protected Areas and Species:
Certain zones are designated as wildlife refuges where hunting is not allowed. Similarly, endangered or vulnerable species are protected by law. Hunters must be informed about which animals they can and cannot target in a given region.
III. Positive Impacts on Hunters
Understanding how game conservation laws affect hunters reveals several advantages beyond wildlife protection. These laws promote:
1. Sustainable Wildlife Populations
By controlling when and what species can be hunted, these laws ensure animal populations do not decline to dangerous levels. This sustainability guarantees hunting opportunities for future generations.
2. Enhanced Safety
Mandatory hunter education programs and legal equipment standards reduce accidents. Wearing hunter orange and maintaining safe distances from populated areas are common legal requirements that protect everyone.
3. Equal Opportunity
Hunting laws ensure that all hunters, regardless of experience or background, follow the same rules. This fairness levels the playing field and prevents any one group from monopolizing wildlife resources.
4. Contribution to Conservation Funding
Hunters indirectly support conservation through fees for licenses, tags, and taxes on equipment. These funds are critical for habitat restoration, species monitoring, and law enforcement.
IV. Challenges Faced by Hunters
While there are benefits, there are also challenges in how game conservation laws affect hunters:
Limited Access:
Some hunters may find fewer opportunities due to strict seasonal windows or protected areas. This can interfere with cultural traditions or limit food sources for subsistence hunters.
Financial Burden:
Costs associated with multiple permits, gear regulations, and mandatory training can be high, especially for low-income hunters.
Enforcement Pressure:
Game wardens enforce these laws strictly, and violations can lead to hefty fines, confiscation of equipment, or even jail time.
Conflict with Traditional Practices:
In some regions, indigenous or local hunting customs may not align with modern conservation laws, creating tension between communities and regulators.
V. The Role of Hunters in Conservation
Hunters are not just subject to the laws; they are also key players in conservation.
Population Control:
In many ecosystems, predators are absent due to human development. Hunters help manage populations like deer, preventing overgrazing and supporting biodiversity.
Data Collection:
Hunters often report their catches, which helps wildlife agencies gather important data on species numbers and health.
Advocacy and Stewardship:
Many hunters belong to organizations that promote ethical hunting and contribute to conservation projects, showcasing how game conservation laws affect hunters in a positive light.
VI. Case Studies and Regional Perspectives
North America:
The U.S. and Canada have robust hunting regulation systems supported by acts like the Pittman-Robertson Act, which channels taxes from firearms to wildlife management.
International Examples:
Countries in Africa use regulated trophy hunting as a tool for conservation, while strict bans exist in other regions to protect critically endangered species.
Local Insight – Punjab, Pakistan:
In areas like Punjab, community-based conservation has shown success. Local hunters collaborate with authorities to monitor wildlife and adhere to seasonal limits.
VII. Future Outlook
Technological Advances:
GPS-tagged wildlife, drone surveillance, and mobile licensing apps are improving compliance and data collection.
Policy Developments:
There is a growing move toward including local voices in law-making to ensure community support.
Education and Awareness:
Continued public education is vital. Campaigns that show how game conservation laws affect hunters in positive ways can increase compliance and support.
VIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, the question “how do game conservation laws affect hunters” is deeply interconnected with both ethical hunting and wildlife sustainability. These laws provide essential structure, ensure the safety of both humans and animals, and allow hunting traditions to continue in a responsible way. Although challenges exist, the long-term benefits to ecosystems and future hunters are substantial. By understanding and respecting these laws, hunters become active partners in conservation.
Other Articles
Comprehensive Guide to the Jianfan Hemoperfutor IFU
www.free worlderorg: The Ultimate Guide to a Money-Free, Sustainable Future
Culaina Grosaina: A Complete Guide to Its Meaning, Origins, and Modern Relevance
Understanding the 3822 Blossom Terrace Erie PA Water Hook Up Diagram: A Complete Homeowner’s Guide